Many times the hobbyist wants to have a simple, dual power supply for a project. Existing powersupplies may be too big either in power output or physical size. Just a simple Dual Power Supply is required.For most non-critical applications the best and simplest choice for a voltage regulator is the 3-terminal type.The 3 terminals are input, ground and output.
The 78xx & 79xx series can provide up to 1A load current and it have onchip circuitry to prevent damage in the event of over heating or excessive current. That is, the chip simply shuts down rather than blowing out. These regulators are inexpensive, easy to use, and they make it practical to design a system with many PCBs in which an unregulated supply is brought in and regulation is done locally on each circuit board.
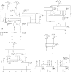
Circuit diagram: 
Dual Power Supply Schematic Circuit diagram
This Dual Power Supply project provides a dual power supply. With the appropriate choice of transformer and 3-terminal voltageregulator pairs you can easily build a small power supply delivering up to one amp at +/- 5V, +/- 9V, +/- 12V, +/-15V or +/-18V. You have to provide the centre tapped transformer and the 3-terminal pair of regulators you want:7805 & 7905, 7809 & 7909, 7812 & 7912, 7815 & 7915or 7818 & 7918.
Note that the + and - regulators do not have to be matched: you can for example, use a +5v and -9V pair. However,the positive regulator must be a 78xx regulator, and the negative a 79xx one. We have built in plenty of safety into this project so it should give many years of continuous service. The user must choose the pair he needs for his particular application.
Parts : 
Transformer
This Dual Power Supply design uses a full wave bridge rectifier coupled with a centre-tapped transformer. A transformer with a power output rated at at least 7VA should be used. The 7VA rating means that the maximum current which can be delivered without overheating will be around 390mA for the 9V+9V tap; 290mA for the 12V+12V and 230mA for the 15V+15V. If the transformer is rated by output RMS-current then the value should be divided by 1.2 to get the current which can be supplied. For example, in this case a 1A RMS can deliver 1/(1.2) or 830mA.
Rectifier
We use an epoxy-packaged 4 amp bridge rectifier with at least a peak reverse voltage of 200V. (Note the part numbers of bridge rectifiers are not standardised so the number are different from different manufacturers.) For safety the diode voltage rating should be at least three to four times that of the transformers secondary voltage. The current rating of the diodes should be twice the maximum load current that will be drawn.
Filter Capacitor
The purpose of the filter capacitor is to smooth out the ripple in the rectified AC voltage. Theresidual amount of ripple is determined by the value of the filer capacitor: the larger the value the smaller the ripple.The 2,200uF is a suitable value for all the voltages generated using this project. The other consideration inchoosing the correct capacitor is its voltage rating. The working voltage of the capacitor has to be greater than thepeak output voltage of the rectifier. For an 18V supply the peak output voltage is 1.4 x 18V, or 25V. So we havechosen a 35V rated capacitor.
Regulators
The unregulated input voltage must always be higher than the regulators output voltage by at least 3V inorder for it to work. If the input/output voltage difference is greater than 3V then the excess potential must bedissipated as heat. Without a heatsink 3 terminal regulators candissipate about 2 watts. A simple calculation of the voltage differential times the current drawn will give the watts tobe dissipated. Over 2 watts a heatsink must be provided. If not then the regulator will automatically turn off if theinternal temperature reaches 150oC. For safety it is always best to use a small heatsink even if you do not think youwill need one.
Stability
C4 & C5 improve the regulators ability to react to sudden changes in load current and to preventuncontrolled oscillations.
Decoupling
The monoblok capacitor C2 & C6 across the output provides high frequency decoupling which keepsthe impedence low at high frequencies.
LED
Two LEDs are provided to show when the output regulated power is on-line. You do not have to use theLEDs if you do not want to. However, the LED on the negative side of the circuit does provide a minimum load tothe 79xx regulator which we found necessary during testing. The negative 3-pin regulators did not like a zeroloadsituation. We have provided a 470R/0.5W resistors as the current limiting resistors for the LEDs.
Diode Protection
These protect mainly against any back emf which may come back into the power supply when itsupplies power to inductive loads. They also provide additional short circuit protection in the case that thepositive output is connected by accident to the negative output. If this happened the usual current limiting shutdownin each regulator may not work as intended. The diodes will short circuit in this case and protect the 2 regulators.
Source :www.electronics-project-design.com