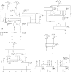
This converter may help if just the serial port on a personal computer is free, whereas the printer needs a parallel (Centronics) port. It converts a serial 2400 baud signal into a parallel signal. The TxD line, pin 3, CTS line, pin 8 and the DSR line, pin 6, of the serial port are used - see diagram. The CTS and DSR signals enable handshaking to be implemented. Since the computer needs real RS232 levels, an adaptation from TTL to RS232 is provided in the converter by a MAX232. This is an integrated level converter that transforms the single +5V supply into a symmetrical ±12V one. The serial-to-parallel conversion is effected by IC1. This is essentially a programmed PIC controller that produces a Centronics compatible signal from a 2400 baud serial signal (eight data bits, no parity, one stop bit). The IC also generates the requisite control signals. If there is a delay on the Centronics port, the RS232 bitstream from the computer may be stopped via the Flow signal (pin 17). This ensures that no data is lost. The controller needs a 4 MHz ceramic resonator, X1.
The serial-to-parallel conversion is effected by IC1. This is essentially a programmed PIC controller that produces a Centronics compatible signal from a 2400 baud serial signal (eight data bits, no parity, one stop bit). The IC also generates the requisite control signals. If there is a delay on the Centronics port, the RS232 bitstream from the computer may be stopped via the Flow signal (pin 17). This ensures that no data is lost. The controller needs a 4 MHz ceramic resonator, X1.
Home » All posts
Monday, September 30, 2013
Serial To Parallel Converter
Thursday, September 26, 2013
Simple Battery Isolator
This circuit is even simpler and employs a 6V feed from one of the stator connections on the vehicle’s alternator. This is connected to a 6V automotive relay (RLY1) which controls a Continuous Duty Solenoid (RLY2). This solenoid electrically connects or isolates the batteries. When the engine is started and the alternator stator voltage rises, the 6V relay turns on. This turns on the Continuous Duty Solenoid to connect the two batteries in parallel. As long as the engine is running, the vehicle’s alternator will maintain charge in both batteries. When the engine is shut down, the alternator stator voltage drops and the Continuous Duty Solenoid switches off, thus isolating the second battery from the vehicle’s electrical system. Provided that camping accessories are only connected to the second battery, the main battery should never discharge. Because the concept is entirely dependent upon the alternator’s stator output voltage, you cannot forget to turn the system on or off as it happens automatically.
When the engine is shut down, the alternator stator voltage drops and the Continuous Duty Solenoid switches off, thus isolating the second battery from the vehicle’s electrical system. Provided that camping accessories are only connected to the second battery, the main battery should never discharge. Because the concept is entirely dependent upon the alternator’s stator output voltage, you cannot forget to turn the system on or off as it happens automatically.
Tuesday, September 24, 2013
AUTOMATIC AIRFLOW DETECTOR ELECTRONIC DIAGRAM
Sensor used in this circuit is a bulb filament. If there is no airflow, the filament resistance would give low value. On the other hand, if there is airflow, the filament resistance would varies. The variation of the resistance is caused by the heat difference between filament. It also effects to the voltage variation passing through that filament. That voltage difference will be processed by LM339 op-amp and displayed by the LED.
Parts list :
- LED1 : LED 5mm
- IC1 volt regulator : LM7805
- Polar Capacitor C1 : 47 uF/15V
- Resistor R1 : 100 ohm
- Resistor R2 : 470 ohm
- Resistor R3 : 10k ohm
- Potensiometer R4 : 100k ohm
- Resistor R5 : 1k ohm
- IC2 op-amp : LM339
- Bulb filament
- Power supply/battery 12V
Sunday, September 22, 2013
Loudspeaker Protector Monitors Current
This circuit uses a 0.1O 1W resistor connected in series with the output of a power amplifier. When the amplifier is delivering 100W into an 8O load, the resistor will be dissipating 1.25W. The resulting temperature rise is sensed by a thermistor which is thermally bonded to the resistor. The thermistor is connected in series with a resistor string which is monitored by the non-inverting (+) inputs of four comparators in an LM339 quad comparator. All of the comparator inverting inputs are connected to an adjustable threshold voltage provided by trimpot VR1. As the thermistor heats up, its resistance increases, raising the voltage along the resistor ladder.
When the voltage on the non-inverting input of each comparator exceeds the voltage at its inverting input, the output switches high and illuminates the relevant LED. NOR gate latches are connected to the outputs of the third and fourth comparators. When the third comparator switches high, the first latch is set, turning on Q1 and relay 1. This switches in an attenuation network (resistors RA & RB) to reduce the power level. However, if the power level is still excessive, comparator 4 will switch, setting its latch and turning on Q2 and relay 2.
This disconnects the loudspeaker load. The thermistor then needs to cool down before normal operation will be restored. The values of R1-R4 depend on the thermistor used. For example, if a thermistor with a resistance of 1.5kO at 25°C is used, then R1 could be around 1.5kO and R2, R3 and R4 would each be 100O (depending the temperature coefficient of the thermistor). The setup procedure involves connecting a sinewave oscillator to the input of the power amplifier and using a dummy load for the output. Set the power level desired and adjust trimpot VR1 to light LED1. Then increase the power to check that the other LEDs light at satisfactory levels.
Friday, September 20, 2013
Fuse Box BMW 328i Central 1999 Diagram
Fuse Box BMW 328i Central 1999 Diagram - Here are new post for Fuse Box BMW 328i Central 1999 Diagram.
Fuse Box BMW 328i Central 1999 Diagram
Fuse Panel Layout Diagram Parts: ABS system, adjustment driver seat, adjusment passenger seat, air bag, air conditioner, blower, brake light, central locking system, cigar lighter, electric fan, electric seat heating, engine control, folding outside mirror, fog light, garage door opener, heated outside mirror, heated rear window, heated spray nozzle, horn, immobilizer, instrument cluster.